Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are both types of organisms. However, they are distinguished by their cell structure. Prokaryotes, or bacteria, have no membrane-enclosed nucleus. Eukaryotes, on the other hand, do have a nucleus that houses their DNA. In this article, we’ll explore the similarities and differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes to see if we can determine if they are indeed the same type of organism or not. Keep reading to find out more.
Are Bacteria Cells Prokaryotic Or Eukaryotic?
Prokaryotic cells are cells that contain a nucleus. Eukaryotes are cells that do not have a nucleus. Bacteria are prokaryotic cells while viruses, fungi, and protozoa are eukaryotic (Vanderford, 2003). Bacteria cells have a cell membrane and an internal region called cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is filled with proteins and lipids that serve as structural components of the cell membrane. The cell membrane is also filled with protein molecules called lipoproteins which carry out the functions of transporting materials between the external environment and the internal milieu of the cell (Vanderford, 2003).
What Is A Eukaryotic Cell?
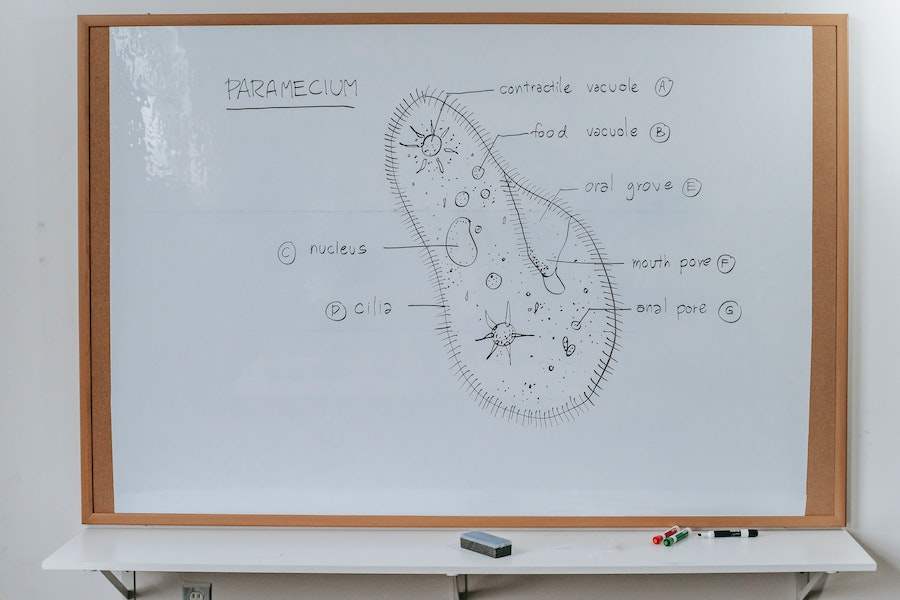
Let’s now turn to a eukaryotic cell. Eukaryotes are cells that have a nucleus and other organelles. They are multicellular organisms and are in all ways similar to the prokaryotes except for one thing: they have a nucleus, and prokaryotes do not. Eukaryotic cells first appeared on Earth over two billion years ago. They are not only found in humans but in all plants, fungi, and algae. Eukaryotic cells are much larger than bacterial cells. They are about 10-100 microns in diameter and have a volume of 10-100 times that of a bacterial cell.
How Are Bacteria And Eukaryotes Alike?
- Bacteria are prokaryotic cells, meaning that they do not have a nucleus or organelles.
- Bacteria are small in size, about 2-5 microns in diameter.
- Bacteria have a very small volume of about 1000 times less than eukaryotic cells.
- Eukaryotes are cells that have a nucleus and other organelles such as mitochondria and ribosomes.
- Eukaryotic cells first appeared on Earth over two billion years ago. They are found in many types of organisms including humans, plants, and fungi, but not animals.
- Eukaryotes generally have a larger volume than bacterial cells (10-100 times the volume).
- Eukaryotes can be multicellular organisms with many parts like plants and animals, but bacteria cannot be multicellular because they do not have mitochondria or nuclei or other organelles like the other cell papillary cells, with a volume of 10-100 times that of a bacterial cell.
- Eukaryotic cells are multicellular organisms and are in all ways similar to prokaryotes except for one thing: they have a nucleus and prokaryotes do not.
- Bacteria and eukaryotes can be found in the same environment, but they do not live in the same environments at the same time because they both require different conditions to thrive.
- Bacteria can be found everywhere, from our bodies to our oceans, while eukaryotic cells are only found in animals and plants.
- Bacteria can survive extreme conditions such as high or low temperatures and low pH values, but eukaryotic cells cannot survive these conditions for very long unless special adaptations allow them to do so like bacteria. all cells.
- Eukaryotic cells have a more complex structure than that bacteria.
- Eukaryotes are multicellular organisms, while bacteria are not.
- Bacteria and eukaryotes are both organisms that exist in all environments, can survive extreme conditions, and thrive in environments that are harmful to human life.
- Bacteria and eukaryotes are both single-celled organisms that live in the body and cause diseases such as anthrax, cholera, salmonella, and tuberculosis (TB).
How Are Bacteria And Eukaryotes Alike?
1. They both have a cell wall and membrane.
These are the two main components of the cell. The cell wall is a barrier that prevents the outside world from getting in. It is made of proteins and is sometimes called a “skin” for bacteria. The membrane is the outer layer of the cell that keeps things inside and protects them from harmful substances like water, salts, and other chemicals.
2. They both have a nucleus (a region inside their cells that contains DNA)
The nucleus holds most of the genetic information in the eukaryotic cell. It also performs many important functions, including cell division and control of gene expression, which determines which genes are active in cells at any given time (see below). The DNA in our cells is wrapped around histone proteins to form chromosomes, which we discussed above. In prokaryotes, this structure (called a nucleoid) is not present; instead, they have DNA floating freely through their cytoplasm.
any of the cellular functions.
3. They both have a cell membrane (an outer layer that surrounds the cell)
The cell membrane is made up of proteins that are embedded in it and help to keep things in and out of the cell.
4. They both have mitochondria (organelles inside cells that produce energy)
The mitochondria are like miniature power plants, producing energy for the body from food molecules. The end product is ATP – Adenosine triphosphate, which is a molecule used by all cells for energy.
5. They both have ribosomes (parts of the cell that make proteins)
The ribosome is an organelle found inside all eukaryotic cells, except chloroplasts, which are found in plants and algae. Ribosomes are responsible for making proteins and mRNA (messenger RNA). mRNA contains instructions that direct protein production, while proteins carry out specific tasks in the cell or act as parts of structures that function in the cell, such as controlling how energy is created and used.
6. They both have a cytoplasm (a fluid-filled region inside the cell)
The cytoplasm is a vital part of the cell. It contains food and waste products, controls how other parts of the cell work, and stores energy.
7. They both have organelles (small structures inside cells)
Organelles help to carry out certain functions in the eukaryotic cell. For example, mitochondria help to produce energy from food by converting it into ATP (adenosine triphosphate). The endoplasmic reticulum is used for protein synthesis. And so on.
8. They both have a cell wall that separates them from their environment
The main purpose of this wall is to protect bacteria from being eaten by predators or having their DNA broken down by harsh conditions like high temperatures or high pressures. This will also help protect.
9. They can live in extreme environments.
Bacteria can survive in harsh and extreme environments ranging from hot water to extreme cold. Bacteria thrive in places that are harmful to human life, such as toxic waste sites or areas with no oxygen. Eukaryotes cannot survive in the same environments since they need oxygen and other nutrients to live.
10. They both have a cell wall and membrane.
The cell wall is a barrier that protects bacteria from harmful substances like water, salts, and other chemicals. The membrane keeps things inside the bacteria cell, protects it from damaging substances, and allows it to absorb nutrients from its environment.
Are Bacteria And Eukaryotes Actually The Same Type Of Organism?
- Eukaryotic cells are multicellular, meaning they have more than one cell. Bacteria are not multicellular.
- Eukaryotes have different organelles like a nucleus and mitochondria (which are like mini-nuclear power plants) that bacteria do not have. Bacteria do not have these organelles.
- Eukaryotic cells are larger in size than bacteria cells, about 10-100 times larger in volume and 10-100 times larger in diameter. Bacteria cells are only 2-5 microns in diameter and 1000 times smaller in volume than eukaryotic cells of the same type of organism (e.g., bacteria versus human).
- Eukaryotic cells contain DNA and proteins, which bacteria do not contain (at least not as a part of their cell).
- Eukaryotic cells have specialized cell membranes that bacteria cells do not have. Bacteria cells do not have these membranes.
Conclusion
Bacteria and eukaryotic cells are both types of organisms. However, they are distinguished by their cell structure. Prokaryotes, or bacteria, have no membrane-enclosed nucleus. Eukaryotes, on the other hand, do have a nucleus that houses their DNA. Eukaryotic cells are larger than bacterial cells and have a nucleus that bacteria do not. This suggests that bacteria and eukaryotes are not the same types of organisms. That being said, there are some similarities between the two types of organisms, including the presence of a cellular membrane, DNA, and a cytoskeleton. However, there are also significant differences between bacteria and eukaryotes, including the presence of the nucleus in the eukaryotes and its absence in the bacteria.