The use of charcoal has been a fundamental part of human history, serving as a versatile and indispensable resource in various aspects of life. From ancient civilizations to modern industries, charcoal has played a pivotal role as a source of energy, a tool for cooking, and a vital component in countless processes. Despite its ubiquity, many are left wondering, “What is charcoal made of?” This curiosity stems from the desire to comprehend the composition of this black, carbon-rich substance and appreciate its significance. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricate world of charcoal, exploring its production, composition, types, applications, and the environmental considerations that surround it. By the end, you’ll have a profound understanding of what charcoal truly is and why it matters.
What Is Charcoal Made Of?
Charcoal is primarily made of carbon, with a minimal amount of volatile matter and ash content. It is produced through a process called carbonization, which involves heating organic materials like wood, peat, coconut shells, or sawdust in the absence of oxygen. This drives off the volatile components, leaving behind a carbon-rich substance with excellent fuel properties and various practical applications.
How Is Charcoal Made?
Charcoal is made through a process called carbonization, which involves the controlled heating of organic materials, such as wood, peat, coconut shells, or sawdust, in the absence of oxygen. The steps involved in charcoal production are as follows:
Selection Of Raw Materials: Suitable organic materials are chosen, depending on the desired charcoal type and its intended use.
Carbonization Process: The selected materials are placed in a closed container or kiln and heated to high temperatures, typically between 600°C and 900°C. During this process, volatile components like water, tar, and gases are driven off, leaving behind carbon-rich char.
Cooling And Collection: Once the carbonization process is complete, the kiln or container is cooled slowly to prevent the char from combusting. The resulting material is then collected as charcoal.
Different Types Of Charcoal Available
There are various types of charcoal available, each with unique characteristics and suitable for specific purposes. Some of the most common types include:
- Lump Charcoal: Lump charcoal is made from hardwood, such as oak, hickory, or maple. It is known for its purity and high carbon content, making it an excellent choice for grilling and smoking food. Lump charcoal burns hot and produces minimal ash.
- Charcoal Briquettes: Charcoal briquettes are widely used for grilling and are made from a combination of charcoal, binders, and fillers. They are uniform in size and shape, burn consistently, and are often more affordable than lump charcoal.
- Activated Charcoal: Activated charcoal is a highly porous form of carbon that has been processed to have a large surface area. It is used for various purposes, including water purification, air filtration, medical applications, and even as a dietary supplement due to its adsorption properties.
- Biochar: Biochar is a type of charcoal specifically produced for agricultural use. It is created by pyrolyzing organic materials like agricultural waste or wood chips. Biochar can improve soil quality, enhance nutrient retention, and promote plant growth.
- Coconut Shell Charcoal: Made from coconut shells, this type of charcoal is prized for its sustainability and mild flavor. It is often used in hookahs, barbecue grills, and as a fuel source for various industrial applications.
- Bamboo Charcoal: Bamboo charcoal is produced from bamboo plants and is known for its high porosity. It is used for air purification, water filtration, and as a component in beauty and wellness products.
- Japanese Binchotan Charcoal: Binchotan is a traditional Japanese charcoal made from oak wood. It burns at high temperatures and is favored for its long-lasting, clean-burning properties, making it ideal for grilling and cooking.
- Art Charcoal: Compressed charcoal sticks or pencils are used by artists for drawing and sketching. These charcoals are designed to produce dark, rich lines with varying degrees of hardness.
Why Charcoal Matters?
Charcoal matters for several important reasons across various industries and applications:
- Energy Production: Charcoal serves as a valuable source of energy, especially in regions where other fuel sources are scarce or expensive. It is used for heating, cooking, and as a fuel in industries like metallurgy and blacksmithing.
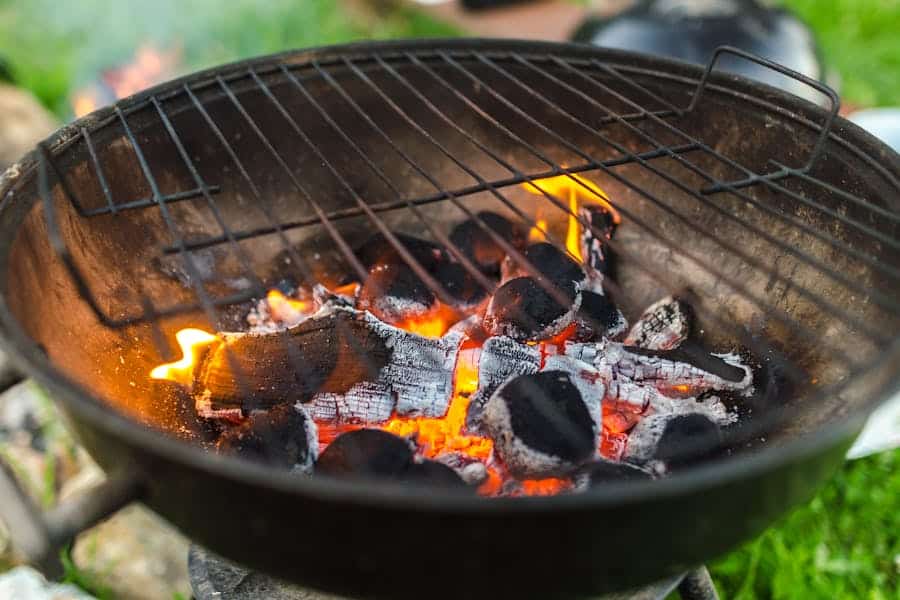
- Cooking Fuel: Charcoal is a popular choice for grilling and outdoor cooking due to its high heat output and ability to impart a smoky flavor to food. It provides a consistent and controllable heat source for a variety of culinary applications.
- Metallurgy And Chemical Industries: In metallurgical processes, charcoal is used as a reducing agent to extract metals from ores. It is also employed in chemical industries for the production of activated carbon and as a carbon source in chemical reactions.
- Art And Culture: Artists use charcoal as a versatile drawing and sketching medium, creating a wide range of artistic expressions. Additionally, charcoal has cultural significance in traditional ceremonies and rituals in various cultures worldwide.
- Environmental Applications: Activated charcoal is crucial for air and water purification. It effectively adsorbs pollutants, toxins, and impurities, making it an essential component in air filters, water treatment systems, and even personal health products.
- Agriculture And Gardening: Biochar, a type of charcoal, enhances soil fertility and promotes plant growth. It helps improve soil structure, retains nutrients, and increases water-holding capacity, leading to better crop yields and sustainable farming practices.
- Traditional And Indigenous Practices: Charcoal has been used in traditional healing practices, such as poultices and charcoal-based remedies, for its potential detoxifying properties.
When And Where Is Charcoal Used?
Charcoal is used in various places and at different times, spanning historical and contemporary contexts, with diverse applications. Here’s a breakdown of when and where charcoal is commonly used:
1. Historical Uses:
Ancient Cooking: Charcoal has been used for cooking since ancient times, providing a reliable heat source for preparing food.
Metallurgy: Historical metalworkers used charcoal as a key ingredient for smelting and forging metals.
Art And Writing: Charcoal has been a traditional drawing and writing medium for artists and scribes throughout history.
Rituals And Ceremonies: In many cultures, charcoal played a significant role in ceremonial and spiritual practices.
Medicine: Historically, charcoal was used for medicinal purposes, such as poultices and wound treatment.
2. Contemporary Applications:
Outdoor Grilling: Charcoal grills are popular for barbecues and outdoor cooking, providing a unique smoky flavor to grilled food.
Industrial And Manufacturing: Charcoal is used in various industrial processes, such as metallurgy, chemical production, and as a fuel in manufacturing.
Air And Water Purification: Activated charcoal is employed in air and water filtration systems to remove impurities and pollutants.
Gardening And Agriculture: Biochar, a type of charcoal, is used to improve soil fertility, water retention, and crop yields.
Artistic Expression: Charcoal remains a preferred medium for artists, allowing for expressive and versatile drawing and sketching.
Environmental Cleanup: Charcoal is used to mitigate environmental disasters like oil spills, where it can adsorb and remove contaminants.
Alternative Fuel: In regions with limited access to traditional fuels, charcoal serves as a reliable source of energy for heating and cooking.
Personal Care And Wellness: Activated charcoal is found in various personal care products, including toothpaste and face masks, for its purifying and detoxifying properties.
Conclusion
In conclusion, charcoal, with its rich history and diverse applications, remains an essential resource in our lives. From cooking and metallurgy to art and environmental cleanup, charcoal plays a pivotal role across various industries and cultures. However, as we harness its benefits, it’s crucial to embrace sustainable practices and consider its environmental impact. By responsibly sourcing and using charcoal, we can ensure its continued relevance and contribution to our society while preserving our natural resources for future generations. Charcoal’s versatility and significance underscore its enduring importance in our world today.
FAQ’s
What Is The Difference Between Lump Charcoal And Charcoal Briquettes?
Lump charcoal is made from hardwood and is pure with no additives, while charcoal briquettes are a mix of charcoal, binders, and fillers.
Is Charcoal Environmentally Friendly?
The environmental impact of charcoal production can vary, but sustainable practices, like using certified wood sources, can reduce its ecological footprint.
How Is Activated Charcoal Different From Regular Charcoal?
Activated charcoal is processed to have a high surface area and is used for adsorption purposes, while regular charcoal is mainly used for fuel and grilling.
Can Charcoal Be Reused?
Yes, charcoal can be reused for grilling by extinguishing the flames and storing it in a dry place for future use.
Is Biochar The Same As Regular Charcoal?
Biochar is a specific type of charcoal produced for agricultural purposes, designed to improve soil quality and enhance plant growth.